
OVERVIEW of ARTIFICIAL LIFT – Part 1
Introduction
Most oil and gas wells at some point in their productive lives would require some form of support to continue to produce at high enough rates to be profitable. To compensate for the lack of natural energy in these formations, proper artificial lift selection, design, implementation, and operation for producing well completions are critical factors in achieving both optimum production rate control over time.
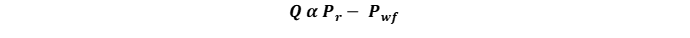
Artificial lift is a method used to lower the producing bottom hole pressure (FBHP) at the sand-face to obtain a higher production rate from the well.
Types of Artificial Lift
Artificial lift systems can be classified into two basic types: Gas lift system or Pump-assisted lift or pumping methods.
Gas Lift System
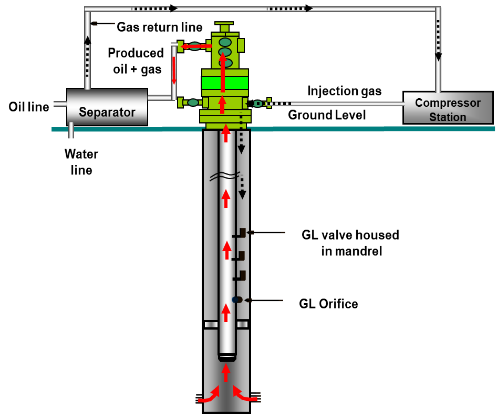
Gas lift technology increases oil production and improves liquid flow in two ways:
- Gas energy of expansion pushes the oil to the surface.
- Gas aerates the oil so that the effective density of the fluid is less, while the bottom hole pressure is reduced.
Pump-Assisted Lift or Pumping Methods
In this case, the reservoir pressure is the driving energy to push fluid to the pump suction intake. The pump then raises the fluid pressure to drive it up to the wellhead, and into the surface facility. This artificial lift method can be further classified into two categories.
1. A Positive Displacement Pump – works by moving fluid from a suction chamber to a discharge chamber. e.g., Reciprocating Rod Pumps, Hydraulic Piston Pumps and Progressive Cavity Pumps (PCPs).
2. A Dynamic Displacement Pump – works by causing fluid to move from inlet to outlet under its own momentum. e.g., Electrical Submersible Pumps (ESP) and Hydraulic Jet Pumps.
Artificial Lift Type Selection – What to consider
Careful consideration of the current and future well conditions is very important in selecting an artificial method to adopt. It is also important to note that there is no single techniques that can provide a quick and easy solution.
Engineering Considerations:
- Expected well production rate over time.
- Anticipated GOR/GLR over the life of the well.
- Anticipated water cut
- Well location
- Hole geometry/deviation
- Sand production
- Casing/tubing restrictions
- Scale tendencies
| To Learn More about Artificial Lift Design using NODAL analysis attend one of the our related courses: Integrated_Production_Modelling and Artificial_Lift_Design&Production_Optimization. Accrete can also support your integrated asset modelling projects executed to achieve defined engineering and business objectives. |
Key Points
There is no “one-size-fits-all” solution to artificial lift related problems
| Artificial Lift Types | Click on our SERVICES for more information |
| Sucker-rod (beam) Pumping Electric submersible pumping (ESP) Gas Lift Hydraulic Pumping Plunger Lift Progressive Cavity Pumps (PCP) | Software Deployment Consultancy Training Engineering Services |
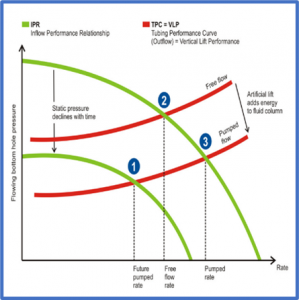
NODAL ANALYSIS PLOT
© 2021 ACCRETE PETROLEUM LIMITED
